Threat actors are now installing a new ransomware called ‘DEARCRY’ after hacking into Microsoft Exchange servers using the recently disclosed ProxyLogon vulnerabilities.
Since Microsoft revealed earlier this month that threat actors were compromising Microsoft Exchange servers using new zero-day ProxyLogon vulnerabilities, a significant concern has been when threat actors would use it to deploy ransomware.
Unfortunately, tonight our fears became a reality, and threat actors are using the vulnerabilities to install the DearCry ransomware.
The DearCry ransomware
According to Michael Gillespie, the creator of the ransomware identification site ID-Ransomware, starting on March 9, users began submitting a new ransom note and encrypted files to his system.
After reviewing the submissions, Gillespie discovered that users submitted almost all of them from Microsoft Exchange servers.
On March 9, a victim also created a forum topic in the BleepingComputer forums where they state their Microsoft Exchange server was compromised using the ProxyLogon vulnerabilities, with the DearCry ransomware being the payload.
After publishing our story, Microsoft has confirmed that the DearCry ransomware is installed in human-operated attacks on Microsoft Exchange servers using the ProxyLogon vulnerabilities.
MalwareHunterTeam was able to find three samples of this ransomware on VirusTotal [1, 2, 3], all of which are MingW-compiled executables. The one analyzed by BleepingComputer includes the following PDB path:
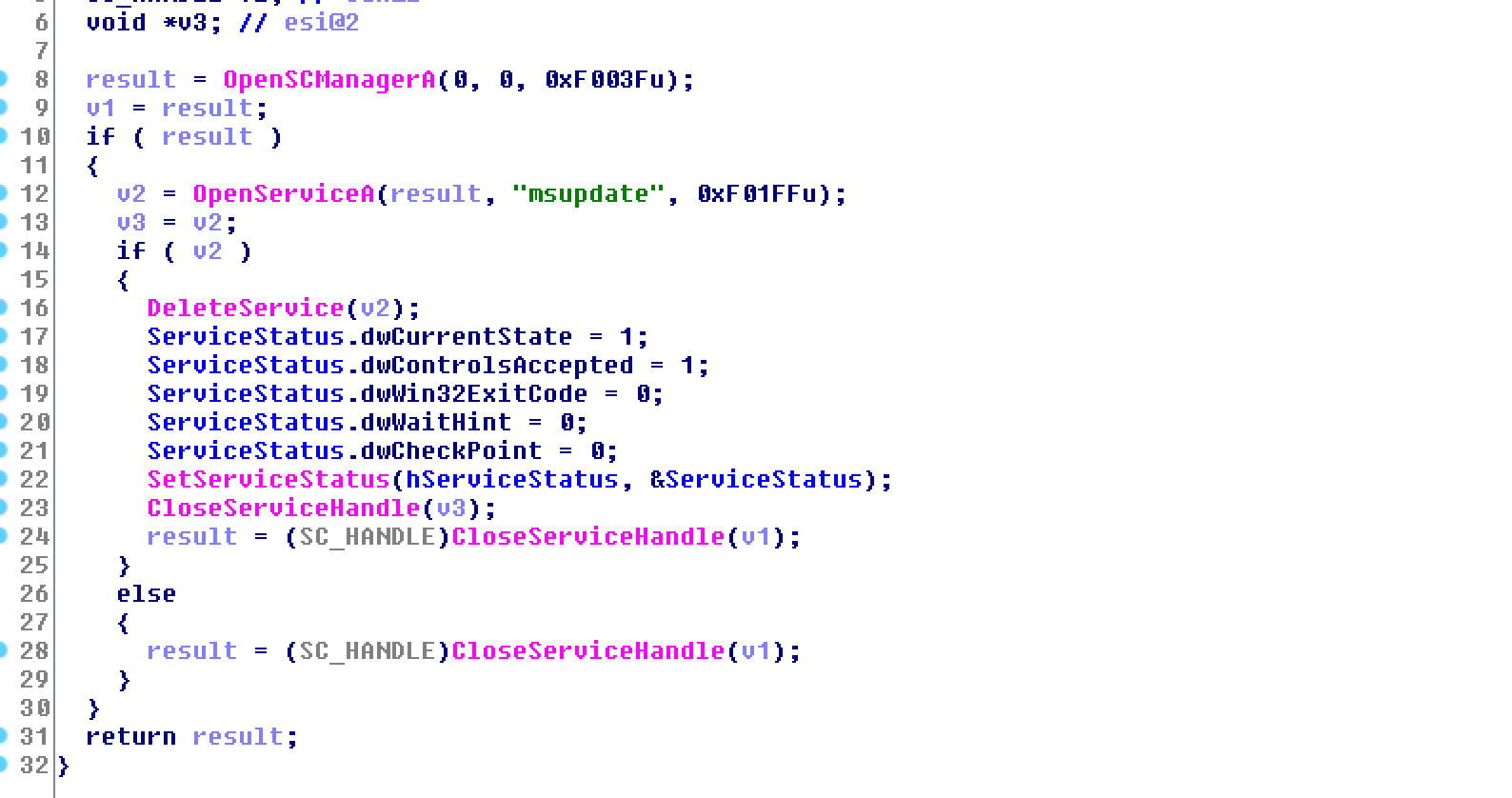
C:\Users\john\Documents\Visual Studio 2008\Projects\EncryptFile -svcV2\Release\EncryptFile.exe.pdbAccording to Advanced Intel’s Vitali Kremez, when launched, the DearCry ransomware will attempt to shut down a Windows service named ‘msupdate.’ It is not known what this service is, but it does not appear to be a legitimate Windows service.
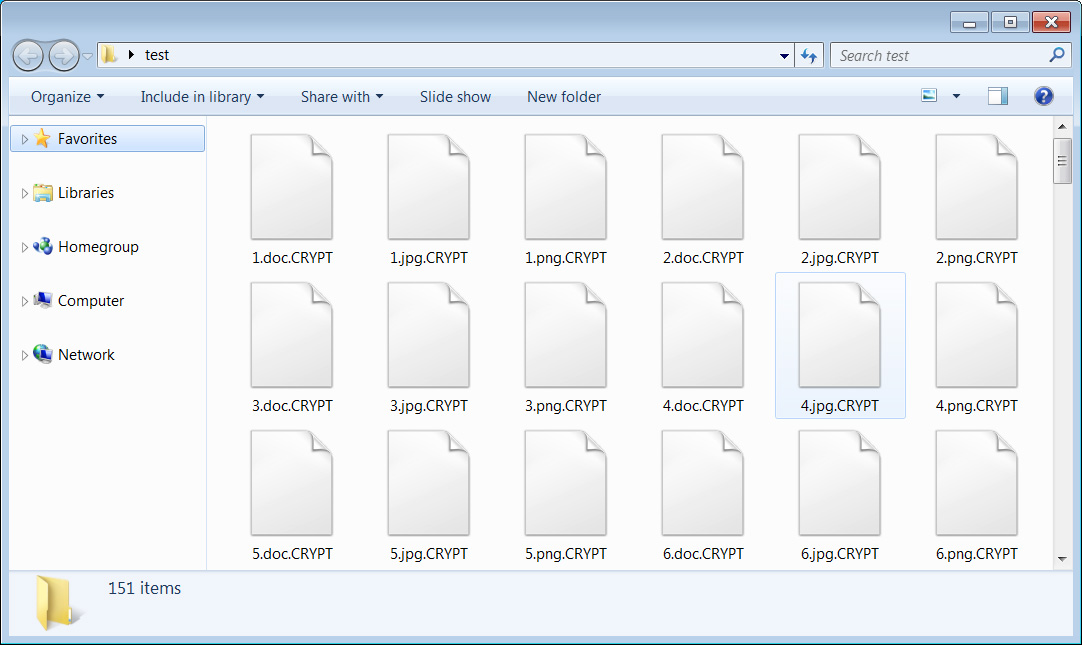
The ransomware will now begin to encrypt the files on the computer. When encrypting files, it will append the .CRYPT extension the file’s name, as shown below.
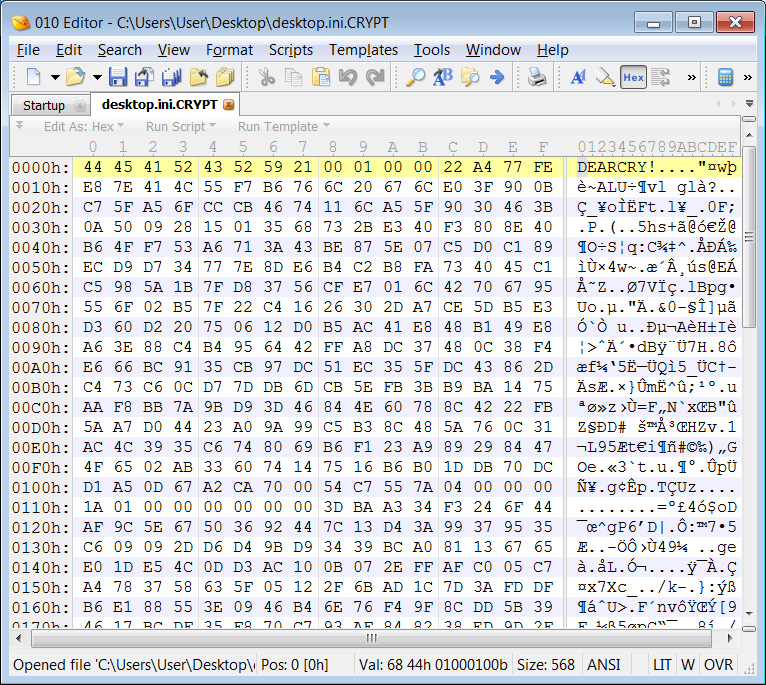
Gillespie told BleepingComputer that the ransomware uses AES-256 + RSA-2048 to encrypt the files and prepends the ‘DEARCRY!’ string to the beginning of each encrypted file.
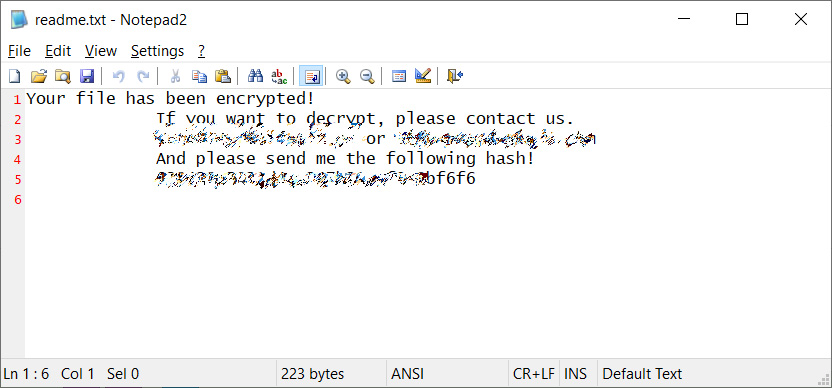
When done encrypting the computer, the ransomware will create a simple ransom note named ‘readme.txt’ on the Windows desktop. This ransom note contains two email addresses for the threat actors and a unique hash, which Gillespie states is an MD4 hash of the RSA public key.
For at least one of the victims, the ransomware group demanded a $16,000 ransom.
Unfortunately, the ransomware does not appear to have any weaknesses that would allow victims to recover their files for free.
Patch now!
While DearCry is not 100% confirmed to be installed via the Microsoft Exchange ProxyLogon vulnerabilities, there is a good chance that it is based on the information at hand.
According to new data shared by cybersecurity firm Palo Alto Networks with BleepingComputer, tens of thousands of Microsoft Exchange servers have been patched over the last three days.
Unfortunately, Palo Alto Networks states that there are still approximately 80,000 older servers that cannot directly apply the recent security updates.
“I’ve never seen security patch rates this high for any system, much less one as widely deployed as Microsoft Exchange,” said Matt Kraning, Chief Technology Officer, Cortex at Palo Alto Networks. “Still, we urge organizations running all versions of Exchange to assume they were compromised before they patched their systems, because we know attackers were exploiting these zero-day vulnerabilities in the wild for at least two months before Microsoft released the patches on March 2.”
All organizations are strongly advised to apply the patches as soon as possible.
Not only to protect your mailboxes from being stolen but now to prevent them from being encrypted.
Update 3/11/21: Updated article after confirmation from Microsoft that it is installed via ProxyLogon vulnerabilities.
To read the original article:



